What is prosthetic dental treatment?
According to the number of missing teeth in the mouth and their location; It is one of the important and big branches of dentistry, which aims to provide oral integrity by eliminating these deficiencies, not only aesthetic but also chewing functions, speaking properly and eliminating psychological problems caused by toothlessness.
What are the types of prosthesis?
Prostheses in general; We can group them as fixed, removable and implant-supported prostheses.
1-FIXED PROSTHESES
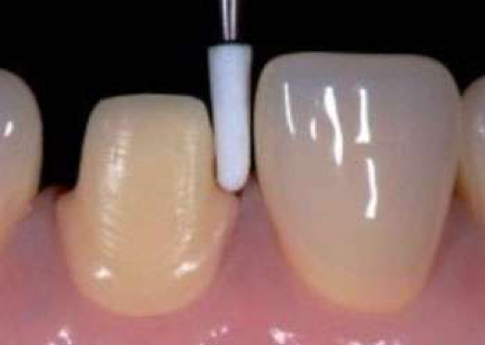
Crown (Coating)
They are coatings made to protect the integrity of the teeth on teeth with excessive material loss such as large bruises and fractures. It is one of the solutions used in the treatment of discoloration of the teeth, closing the spaces between the teeth, aligning the teeth outside the dental arch, or in the treatment of patients who are not satisfied with the appearance of their own teeth. The crown is made by placing it on the slightly reduced teeth.
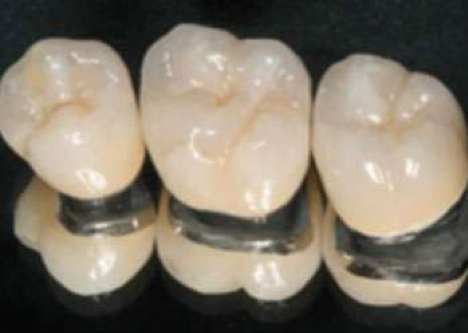
Metal-backed porcelain veneers
The interior of metal-supported porcelain veneers is metal. The metal is put into the form of teeth and covered with porcelain. Although they are high quality products in terms of aesthetics, they can cause naturalness problems in terms of light transmittance.
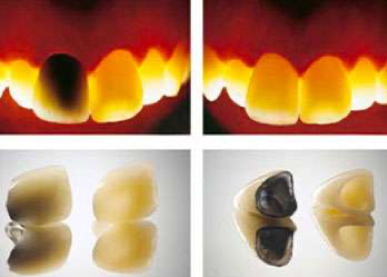
Zirconium supported veneers
Zirconium supported veneers are the aesthetic veneer application with the closest light transmittance to the natural tooth. Zirconium coating is an aesthetic solution that eliminates the risk of allergies, creates a healthier harmony with the gums, and has a much higher light transmittance than metal ceramic coatings. The fact that the color of zirconium is white does not pose a problem in light transmittance in zirconium-supported porcelain coatings like metal-supported coatings. In metal ceramic coatings, obtaining the tooth form as a result of shaping the metal and placing the coating on the metal is behind the zirconium-supported ceramic coatings in light transmittance.
Full ceramic coatings
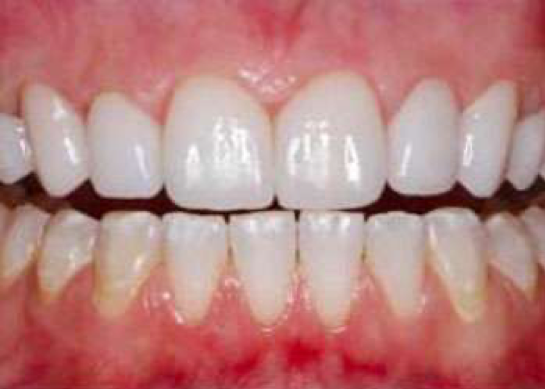
Ceramic or composite lamina crowns are aesthetic applications with a maximum thickness of 0.3 – 0.7 mm, which are applied only from the visible front surfaces of the teeth, without reducing as much as a normal tooth cut, with some abrasion. Composite laminates can be made in a single session while the patient is on the couch, but ceramic laminates are made by our technicians in the office like all other coatings. Since ceramic laminates are made entirely of porcelain, they are more aesthetically successful coatings than composite.
Bridges
In patients with one or more missing teeth, the teeth facing the gap are used as bridge pillars, and the removal of the missing tooth is called bridge applications.
Today, implant treatment is the healthiest way to compensate for tooth loss. In implant applications, they are not damaged, since no action is taken on the neighboring teeth. However, in cases where implant application is not possible, classical solutions such as bridges are still used.
For this type of prosthesis, materials preferred in full dentures are used. Depending on the need, different types of binders can be used in the connection of the prosthesis with the implants in the mouth.
Implant-mounted removable prostheses are a savior for many patients. Removing the movement of the prosthesis gives confidence and comfort to patients who have difficulty getting used to full dentures, patients whose prosthesis moves a lot and who cause discomfort by injuring the palate.
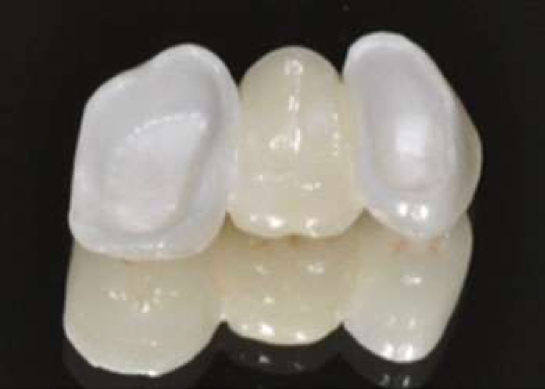
In bridge applications, the materials used in the coating of single teeth are preferred according to different treatment needs. Along with metal ceramic bridges, zirconium ceramic bridges are also frequently used according to aesthetic needs. In anterior tooth deficiencies, full ceramic bridges are another treatment option as they respond to aesthetic needs more than zirconium ceramic bridges.
2-MOVABLE PROSTHESES
Removable prostheses are used to replace missing teeth in patients who have lost all or part of their teeth due to gingival disorders.
Removable prostheses, also known as palate prostheses; It can be done in two different ways, fully or partially.
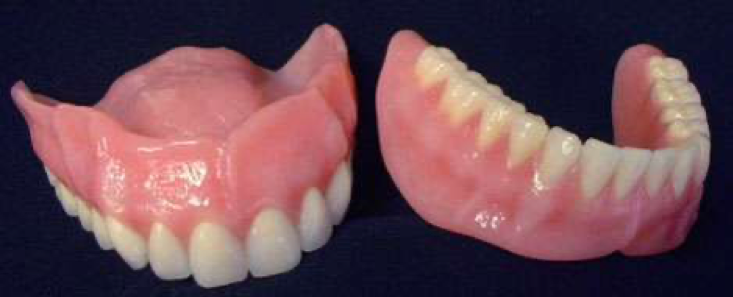
Full dentures are prostheses made of acrylic bases and teeth, which are designed with support from oral tissues for patients who do not have any teeth in their mouths.
Full dentures eliminate aesthetic concerns such as inward shrinkage of the lips, dents in the lower part of the face and aged appearance, especially after all the teeth have been extracted, both restoring chewing functions and providing patient satisfaction by putting an end to aesthetic concerns.
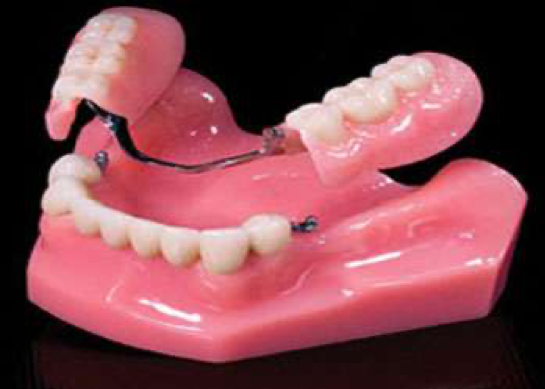
Partially removable dentures are prostheses that are supported by both the teeth in the mouth and the oral tissues, which are used especially in patients who do not have teeth to be used as a fixed prosthetic foot after the removal of the posterior teeth, or who have too many missing teeth to be able to build a bridge.
Since there is no metal appearance in full (palatal) dentures, it does not cause any aesthetic concern, but it may not be possible to say the same for partial removable dentures. Partially removable dentures may cause aesthetic anxiety in the patient as they are attached to the teeth with metal fittings. The solution to this problem is to make the connections made with the teeth invisible by using sensitive connections.
For this type of prosthesis, materials preferred in full dentures are used. Depending on the need, different types of binders can be used in the connection of the prosthesis with the implants in the mouth.
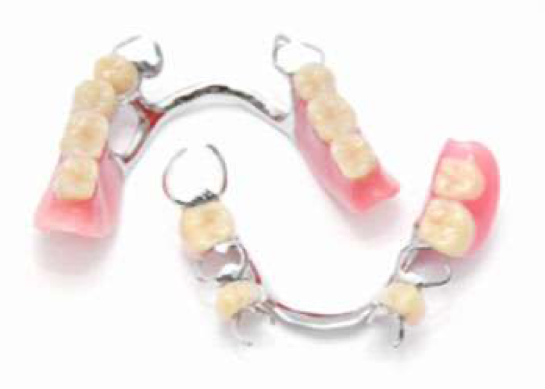
Implant-mounted removable prostheses are a savior for many patients. Removing the movement of the prosthesis gives confidence and comfort to patients who have difficulty getting used to full dentures, patients whose prosthesis moves a lot and who cause discomfort by injuring the palate.
3-IMPLANT PROSTHESES
Implants have become the treatment of the century because of the advantages of eliminating the obligatory practices such as cutting the healthy teeth adjacent to the tooth cavity in the treatment of fixed bridge prosthesis, which is a treatment method for few missing teeth, and being applied only to the space in the cavity and protecting the patient’s healthy tooth integrity.
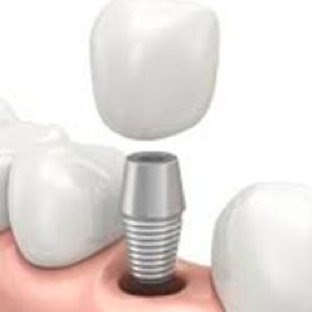
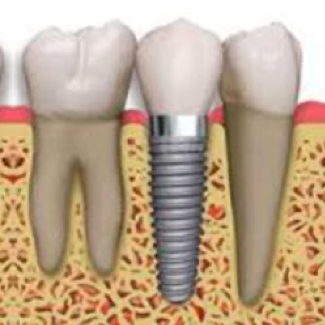
The fact that the implant is actually a tooth root made of titanium also creates the need for a prosthesis to be placed on it. For this reason, the prostheses used in patients whose tooth deficiency is treated with implants are called implant prostheses. It is used in many patients from single tooth deficiency to toothlessness in the entire mouth. Implant prostheses can be made in two different ways, fixed and mobile.
Fixed prostheses on implants
They are prostheses designed according to the number and location of missing teeth (can be made in a number that can vary between a single tooth and a full jaw) and used in a fixed position by sticking. These prostheses can be made of metal ceramic or zirconium ceramic, just like fixed prostheses made on teeth.
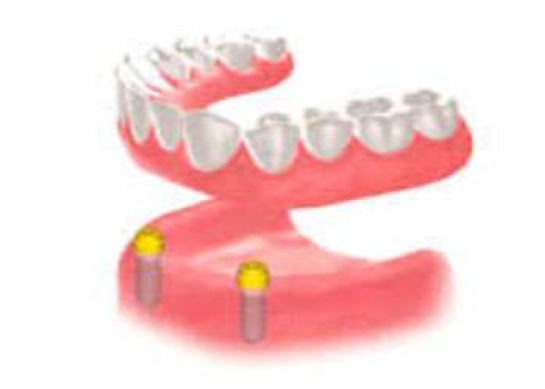
Removable prostheses on implants
On the other hand, removable dentures on implants are prostheses made on implants placed in complete edentulousness, which can be put on and removed by the patient. Particularly in patients using full dentures, lower prostheses may become dislodged as a result of excessive bone resorption. Considering the effect of the tongue and cheeks, it can cause discomfort even when speaking. In this case, if the lower jaw can be implanted, the patient’s lower prosthesis is attached to the implants, preventing movement and discomfort. For this type of prosthesis, the materials preferred in full dentures are used. Depending on the need, different types of binders can be used in the connection of the prosthesis with the implants in the mouth.
Implant-mounted removable prostheses are a savior for many patients. Removing the movement of the prosthesis gives confidence and comfort to patients who have difficulty getting used to full dentures, patients whose prosthesis moves a lot and who cause discomfort by injuring the palate.